Calculator
The Calculator window allows simple calculations to be performed on the current data sets to create new data sets.
The window contains the following elements:
- Window Menu — Actions local to the calculator.
- Tool Bar — Actions for the calculator.
- Formula — The current calculation to evaluate.
- The Create button will create a new set of data using the calculation expression; this button is only available if the expression is correct.
- New data sets will use the dates from the first data set present in the formula.
- New data sets are numbered
DataNwhere N counts up from 0, unless a specific name is given in the Name field.
- Results — The first few elements of each set of data used and the results of the calculation.
- Constant list — A list of available constants for calculations.
- Function list — A list of available functions for specific calculations.
Calculator Window Menu
The calculator menu  contains the following specific entries:
contains the following specific entries:
- Hide Tool Bar / Show Tool Bar — Hide or show the tool bar for this window.
- Reset Calculator — Reset the calculator back to its initial state, empties the formula and the results table.
Tool Bar
| Icon | Action |
|---|---|
 |
Function list Show/Hide the table of available calculator functions. |
 |
Constant list Show/Hide the table of available Constants. |
 |
Results preview Show/Hide the results preview table. |
 |
Reset Reset the calculator back to its initial state, empties the Expression and the results table. |
 |
Preferences Open the Calculator preferences tab. |
 |
Help Display the help for the calculator. |
 |
Hide the tool bar Remove the tool bar. (N.B. The tool bar can be restored in the window menu). |
Tip
The tool bar can be placed on any of the edges of the window by dragging it to that edge or pressing the right mouse button on any blank space and selecting an edge on the popup menu.
Calculation Formula
This entry shows the current calculation together with the name and units of the dataset to be created.
The formula can be modified by:
- Using the History List (see below) by pressing the small triangle button to the right of the formula.
-
Typing on the keyboard.
Tip
Use the TAB key to complete dataset or function names
-
Double clicking on the name of a function in the functions table.
- Double clicking on the name of a constant in the constants table.
- Dragging and dropping datasets from the Data Sets window.
 Selecting a dataset from a popup list.
Selecting a dataset from a popup list.
As the calculation is modified, and when the expression is correct the results table will be updated.
If a  is displayed, then the calculation is incorrect and must be modified. An error message indicating the problem is displayed under the Expression.
is displayed, then the calculation is incorrect and must be modified. An error message indicating the problem is displayed under the Expression.
If a  is displayed, then the calculation is not coherent and should be modified (time base is different), new data can still be created. A warning message indicating the problem is displayed under the Expression.
is displayed, then the calculation is not coherent and should be modified (time base is different), new data can still be created. A warning message indicating the problem is displayed under the Expression.
If a 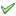 is displayed, then the calculation is a correct expression and a new data set can be created by pressing the Create Data button.
is displayed, then the calculation is a correct expression and a new data set can be created by pressing the Create Data button.
History List
Each time a new set of data is created the calculation expression which was used to generate it is kept in a history list, selecting an entry will replace the current calculation.
Tip
The history list can be emptied and the number of elements kept in the history list can be modified in the Preferences window.
Name
This name will be used for the next data set created with the calculator. See Limitations for the set of acceptable characters.
If this field is empty then the created data set will be numbered 'DataN' where N counts up from 0.
Units
This name will be used as the units for the next data set created with the calculator. See Limitations for the set of acceptable characters.
If this field is empty then the created data set will have 'none' for its units.
Results Preview
This table gives a preview of the dataset values that will be produced, including all the datasets used in the calculation.
The preview, for speed, may process only partial datasets, the results displayed may be diferent when processing the complete datasets (e.g. Filter() or Slice()) for the final calculation.
Tip
The number of elements calculated and displayed in this table can be changed in the Preferences window.
Constants
This table gives a list of numerical constants.
Tip
The list of constants can be updated in the ini file.
Function list
The formula for a calculation can contain mathematic and scalar functions:
Basic Math (in order of Precedence)
| Operator | Description |
|---|---|
( ) |
Parenthesis changes precedence |
^ |
Exponent |
* / % |
Multiply, divide, remainder |
+ - |
Add and subtract |
Scientific Functions
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
abs() |
Absolute value |
sin() cos() tan() |
Sinus, Cosinus, Tangent (Radians) |
asin() acos() atan() |
ArcSinus, ArcCosinus, ArcTangent (Radians) |
sinh() cosh() tanh() |
Hyperbolic Sinus, Tangent, Cosinus (Radians) |
log10() log() exp() |
Log base 10, Natural Log, e to the power of x |
ceil() |
Ceiling (next highest whole number) |
floor() |
Floor (previous lowest whole number) |
norm() |
Scale all values to be between 0.0 and 1.0 |
random() |
Random values from 0.0 to 1.0 |
round() |
Round (nearest whole number) |
sqrt() |
Square root |
Logic Functions
| Operator / Function | Description |
|---|---|
- |
Unary Minus (invert sign) |
! |
Logical NOT (0.0 if non-zero, 1.0 otherwise) |
< > |
Less than, Greater than (1.0 if true, 0.0 otherwise) |
== != |
Equal to, Not equal to (1.0 if true, 0.0 otherwise) |
<= >= |
Less than or equal, Greater than or equal (1.0 if true, 0.0 otherwise) |
&& |
Logical AND (1.0 if both non-zero, 0.0 otherwise) |
|| |
Logical OR (0.0 if both zero, 1.0 otherwise) |
& |
Bitwise AND (integer part) |
| |
Bitwise OR (integer part) |
<< >> |
LeftShift, RightShift (integer part) |
? : |
Ternary operator: (expression) ? TrueVal : FalseVal |
Note: TrueVal/FalseVal can be constant values or expressions containing datasets.
Scalar Functions
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
adev() |
Average deviation of the data elements |
kurtosis() |
Degree of peakedness (fourth moment) |
length() |
Number of data elements |
min() |
Minimum value of all data elements |
max() |
Maximum value of all data elements |
mean() |
Mean average value of data elements |
median() |
Median average value of data elements |
nz() |
Number of zero data elements |
prod() |
Product of the dataset |
q1() |
First quartile of the data elements |
q3() |
Third quartile of the data elements |
sdev() |
Standard deviation of the data elements |
skew() |
Skewness (third moment) of the data elements |
sum() |
Sum of the data set |
variance() |
Variance of the data elements |
Extended Functions
-
AlignX —
AlignX(dataset1,dataset2)Produce a new data set from dataset1 with the same x values as dataset2 by interpolation. -
Atan2() —
Atan2(dataset1,dataset2)Produce a new data set by calculating the ArcTangent for the pair of values (Radians).atan2(n) = atan2(dataset1(n),dataset2(n)) -
Bit() —
Bit(dataset,n)Produce a new data set by extracting the bit number 'n' from each value. Numbering starts from '0'. -
Cumul() —
Cumul(dataset)Produce a new data set by cumulating the values of dataset.cumul(0) = dataset(0)cumul(n) = dataset(n) + dataset(n-1) -
CumulDistrib() —
CumulDistrib(dataset)Produce a new data set by computing the cumulative distribution of dataset.cumul(n) = 100 * count_points_lower_or_equal(dataset(n)) / N -
Delta() —
Delta(dataset)Produce a new data set by calculating the delta of dataset.delta(0) = delta(1)delta(n) = dataset(n) - dataset(n-1) -
DeltaT() —
DeltaT(dataset)Produce a new data set by calculating the delta of date dataset.deltat(0) = 0deltat(n) = date(n) - date(n-1) -
Derive() —
Derive(dataset)Produce a new data set by calculating the derivative of dataset.derive(0) = 0derive(n) = (dataset(n) - dataset(n-1)) / (t(n) - t(n-1)) -
Filter() —
Filter([dataset,] expression)Produce a new data set by copying dataset, for each element where the expression evaluates to TRUE.- Labels must use single quotes (
') to limit the text. - Examples:
Filter(VBAT > 34)— Copy only VBAT values > 34Filter(IBAT, MODEBM == 'I LIMIT')— Copy IBAT values when MODEBM is 'I LIMIT'Filter(DEFICIT, IBAT != 0 && MODEBM == 'TRICKLE')— Copy DEFICIT values when IBAT ≠ 0 and MODEBM is TRICKLE
- Labels must use single quotes (
-
Integ() —
Integ(dataset)Produce a new data set by calculating the integral of dataset.integ(0) = 0integ(n) = (dataset(n) * (t(n)-t(n-1))) + integ(n-1) -
Mean() —
Mean(dataset1, dataset2, ...)Produce a new data set by calculating the mean of a set of datasets.mean(0) = (v1(0)+v2(0)+v3(0)) / 3.0mean(n) = (v1(n)+v2(n)+v3(n)) / 3.0 -
Merge() —
Merge(dataset1, dataset2, ...)Produce a new data set by merging the set of datasets into one. Any double entries (same date, same value) will be removed. -
Norm() —
Norm(v1, [v2, ...])Produce the norm of a set of datasets.Norm(v1, v2) = sqrt(v1^2 + v2^2) -
Reduce() —
Reduce(dataset)Produce a new data set by reducing intermediate repeated values to only the first and last values. -
Slice() —
Slice(dataset,n,m)Produce a new data set using the values from the range indicated by the indexes n and m. (¹) -
SliceTime() —
SliceTime(dataset, t1, t2)Produce a new data set using the time range t1 - t2 of dataset.The range is from the first t1 limit to the last t2 limit; if the dataset is not in chronological order, the result may include dates outside the range t1-t2 (See Sorting).
- Calendar dates must use single quotes (
') to limit the text. - Example:
SliceTime(VBAT, '2003/05/28 18:00:23.917', '2003/05/28 18:59:35.944')
- Calendar dates must use single quotes (
-
Smooth —
Smooth(dataset,order)Produce a new data set using dataset smoothed using the order-n, where0 < order < (dataset length /2). -
Transition() —
Transition(dataset)Produce a new data set by reducing multiple repeated values to only one instance, leaving only transitions. -
Using-X —
UsingX(dataset1,dataset2)Produce a new data set using dataset1 for the Y values and dataset2 for the X values.As long as dataset2 is loaded in PrestoPlot, its date values will be visible in the new datasets tooltips and Data Table and can be displayed in POINT and 2POINT Markers.